Color Analysis : How do colors affect your look?
- Color Theory & COLOR ANALYSIS (components, combinations, seasons etc.)
- HOW TO FIND YOUR SKIN UNDERTONE
- Primary (4 Season) Seasonal Color Analysis
- Flow (12 season) Seasonal Color Analysis

The Power of Color!
Have you ever noticed that certain clothing colors make you look tired and washed out while others instantly make you look fabulous?
The right colors bring your natural appearance to life and enhance your skin, eyes, and hair. Right colors do not take over your look; they connect you and create harmony with your face. Right colors also reduce imperfections such as dark circles and lines under your eyes and bring a brighter and healthier appearance; you may not need a lot of makeup.
When wearing these colors, your skin looks rosy and glowing, your jawline narrower and lifted, your eyes bright and sparkling, and your hair shiny and intense.
Some colors make you look tired and washed out, emphasize shadows on your face, and make your skin tone appear uneven. Wrong colors can make you look tired, emphasize dark circles under your eyes, create blemishes, and dull your hair and complexion.
But what makes a color look fabulous on you?
Certain colors will look great on you if they share the same color dimensions (temperature/undertone, value, and chroma) as your natural coloring. Your natural coloring, as seen in your skin, eyes, and hair, forms a unique palette. Colors that complement these aspects will enhance your natural beauty and make you look fantastic.
Color Theory & Color Analysis
Before we begin to our in-dept color analysis, we need to know the components of color theory. The color wheel was invented in 1666 by Isaac Newton, who mapped the color spectrum onto a circle. The color wheel is the basis of color theory, because it shows the relationship between colors.
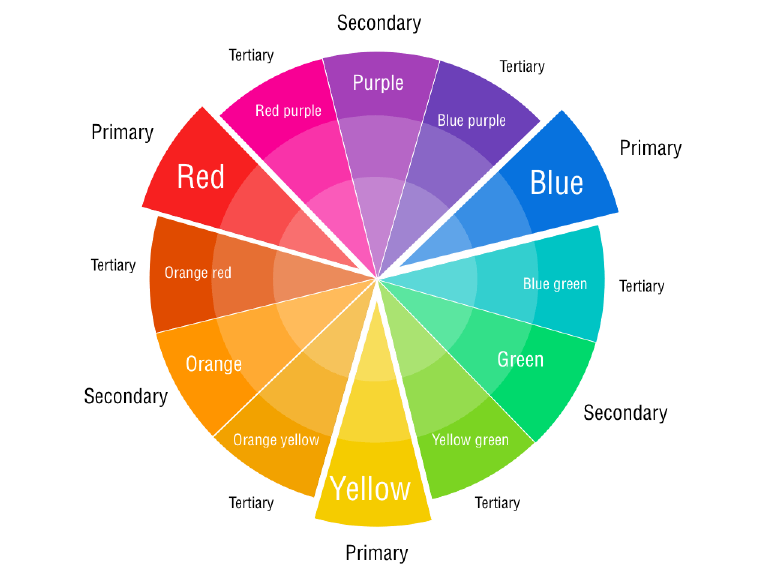
Primary colors are colors that can’t be mixed with other colors. There are 3 primary colors: red, yellow, and blue.
Secondary colors are colors that result from mixing two primary colors. There are 3 secondary colors: purple (red mixed with blue), orange (red mixed with yellow), and green (yellow mixed with blue).
Tertiary colors are colors made by combining a secondary color with a primary color. There are 6 tertiary colors : red-orange (vermillion), yellow-orange (amber) , yellow-green (chartreuse) , blue-green (teal) , blue-purple (violet) , and red-purple (magenta)
Hue, Shade, Tint & Tone

A hue is basically any color on the color wheel, the pure form of the color.

A shade is created by adding black to a base hue, darkening the color. This creates a deeper, richer color.
A tint is created by adding white to a base hue, lightening the color. This can make a color lighter and less intense.
A tone is created by combining grey with a base hue. Like tints, tones are subtler versions of the original color. It defines the colour for being bright/clear or muted/soft/smoky.
Color Combinations

COMPLEMENTARY
Two colors that are on opposite sides of the color wheel. Provides a high contrast , therefore these colors will appear brighter and more prominent.

MONOCHROMATIC
Three shades, tones and tints of one base color. Provides a subtle and conservative color combination and creates a harmonious look.

ANALOGOUS
Three colors that are side by side on the color wheel. Better to use one dominant color and use the others as accent colors in order to balance the look.

TRIADIC
Three colors that are evenly spaced on the color wheel. This provides a high contrast color scheme and creates bold, vibrant look.

TETRADIC
Four colors that are evenly spaced on the color wheel. Better to use one dominant color and use the others as accent colors in order to balance the look, it has a bold and vibrant appearance.
Color Analysis Components
1. Color Temperature/Undertone
The color wheel is divided into warm and cool colors. The warmth or coolness of a color is also known as its color temperature.
Warm colors are the colors from red through to yellow. Cool colors are the colors from blue to green and purple. For general ruler, YELLOW is the WARMEST color while BLUE is the COLDEST.
This does not mean that every blue is cool or every yellow is warm. Every color has different undertones can be cool or warm.

2. Luminance/Value/Contrast/Dept
It is the amount of brightness or light in a color. The scale is between light and dark/deep.

3.Saturation/Chroma/Clarity/Intensity/Tone
It is the intensity or purity of the color. The scale is between muted/soft and bright/clear.

Seasonal Colors
Seasional Color Analysis is the most widely used colour analysis. Seasonal colors are hues that mirror the shades seen in the four seasons of nature.
WINTER
WINTER COLORS are cool and icy, has shades and tints (white and black added to pure color forms).





SPRING
SPRING COLORS are bright, warm and tinted (white added to the pure color form),





SUMMER
SUMMER COLORS are soft, muted and toned (grey added to the pure color forms) ;





AUTUMN
AUTUMN COLORS are golden and earthy, has shades and tones (black and grey added to pure color forms)





Universal Colors
There are some colors and neutrals called “universal colors.” These are the colors anyone can wear because their color dimensions are fairly neutral - meaning they are neither too cool nor too warm, neither too dark nor too light, and neither too bright nor too muted. These colors have neutral undertones with medium value and intensity, making them suitable for most people.
The universal colors don’t look terrible on anyone, but they may not be your most flattering colors, either! So, if you’re looking for a color that won’t be bad for anyone for a uniform, bridesmaid dress, etc., you can choose universal colors.
Universal colors are : charcoal brown/taupe, navy, watermelon red, jade green, turquoise, teal, cobalt blue, deep periwinkle, medium purple, warm pink, stone gray and soft white.












Skin Undertone & Overtone
Determining your skin undertone involves recognizing color undertones:
Yellow undertones are considered WARM, blue undertones are COOL, and red undertones fall in the middle as NEUTRAL.
Colors between blue and red are NEUTRAL COOL (purple undertones), while those between yellow and red are NEUTRAL WARM (orange undertones).
The coloring of your appearance: the color of your skin, hair, and eyes are all the result of the unique combination of melanin (black, blue, brown) and carotene (yellow, orange, red) levels.
Skin undertone refers to the underlying color of your skin tone. It can be anywhere on the spectrum, from cool (blue) through neutral (red) to warm (yellow).
Whether your skin is light or dark is not relevant to the concept of skin undertone. What is essential is whether it is warm or cool.
On the other hand, skin overtone is the overlaying color of your skin. Overtones range from fair to deep.
Warm Undertones (fair to deep)

Cool Undertones (fair to deep)

Neutral Undertones (fair to deep)

How To Find Your Skin Undertone : Warm or Cool ?
The simplest test to understand your skin temperature uses a plain white piece of paper. Hold a white paper next to your face in natural light and compare how your skin looks in contrast to the paper.
If your skin appears gray, pink, or blueish, then you are COOL; if it appears yellowish or peachy, then you are WARM.
How does your skin react to the sun? People who tan easily instead of burn usually have warm skin tones. People who burn rather than tan usually have cool skin tones.
COOL

WARM

Next, flip your hand palm up and take a peek at the veins in the hand and wrist. If your veins appear to be blue or purple, you have cool skin. If they appear green, then you have warm skin. If it's hard to tell one way or the other what color they favor, then you have neutral skin.


The most popular is a metal test. Do you look better in gold or silver? If gold suits you, you have warm undertones. If silver looks good on you, your undertones are cool. And if both metals look fine on you, you have neutral undertones. Warm skin clashes with silver and looks greenish and muddy because it has yellow undertones. Cool skin has the same effect when you bring gold near it because it has blue undertones.
Primary (4 Season) Seasonal Color Analysis
Seasonal Color Analysis consists of 4 to 16 categories depending on which theory is used. Each category has its matching color palette. Primary Seasonal Color Analysis represents 4 seasons; while Flow Seasonal Color Analysis represents 12 or 16 color categories.
Primary Seasonal Color Analysis represents 4 color categories which are named after seasons: Winter, Spring, Summer and Autumn.
This analysis focuses on two dimensions:
1.Temperature /Undertone : WARM-yellow based or COOL-blue based
2.Value/Contrast : DARK/DEEP, MEDIUM or LIGHT

These color dimensions are used to represent two basic variables:
Undertone of your skin, hair and eyes (WARM/golden/yellow or COOL/blue/pink)
Your overall natural coloring (DARK or LIGHT)
Warm Undertones
Warm Skin Tones : yellow, golden, and peachy undertones
Warm Eye Colors : Brown, hazel, olive green, amber, warm blue; mostly brighter and lighter than cool eyes
Warm Natural Hair Colors : Brown (Light to dark golden tones), Blonde (golden or strawberry); red (ginger, copper, auburn)
Cool Undertones
Cool Skin Tones : blue, gray, and pink undertones
Cool Eye Colors : Blue, gray, bright green, cool brown; mostly soft, grayish, and dark
Cool Natural Hair Colors : Brown (light to dark ashy tones), Blonde (ash, sand, platinum), Black, Silver, Gray, Dark Auburn
Neutral Undertones
Neutral Skin Tones : peachy pink and red undertones
Neutral undertones are balanced between yellow and blue and are the most versatile. If you have a neutral undertone, your undertones are roughly the same color as your actual skin tone. There are three categories for Neutral: Full Neutral, Neutral-Warm, and Neutral Cool.
Value & Contrast
Value refers to the lightness or darkness of a color. When you incorporate more black into a color, it deepens and becomes darker. Conversely, when you introduce more white to a color, it lightens and brightens.
In the context of seasonal colour analysis, determining the contrast level of a person's overall colouring involves considering two essential factors: value contrast and hue contrast.
Value Contrast: This measures the difference between the darkness or lightness of a person's hair, skin, and eyes. High contrast means significant differences, while low contrast indicates minimal differences.
Hue Contrast : You can also assess contrast by considering the separation between two colors on the color wheel. When two hues are positioned on opposite sides of the color wheel, they will exhibit a very high level of contrast.
To determine the contrast value of your personal colouring, convert a photo of your face into grayscale. Take note of the distribution of values in the image; observe whether they meld together seamlessly or if there are discernible areas of both light and dark, which will help you ascertain the degree of contrast in your appearance.
Individuals with a light value have similarly light hair, skin and eyes. This creates a low contrast between the features. Individuals with a deep value exhibit prominent dark hair and eyes, creating a distinct contrast with their relatively lighter skin. This contrast between their features is considered to be high. People with a medium value do not possess notably light or dark features. All their characteristics share a similar medium colouring, resulting in an overall medium level of contrast between them.
Seasonal Color Analysis : Primary Seasons
There are four possible results according to this method:
If you have cool skin tone, you would be either Winter or Summer:
If your natural hair has darker tones, you would fall into WINTER color palette,
If your hair has lighter tones, than you would have SUMMER color palette.
If you have warm skin tone, you would be either Spring or Autumn.
If your natural hair has darker tones, you would fall into AUTUMN color palette.
If your hair has lighter tones, than you would have SPRING color palette.

COOL-DEEP-BRIGHT
Cool, Sophisticated, Dramatic, Striking, Brilliant
High Contrast between features
Bright and Clear qualities
Medium to deep hair colours
Blue based, bright, cool skin tones

COOL-MUTED-LIGHT
Soft, Elegant, Smoky, Harmonious, Refined
Low Contrast between features
Light and Smoky qualities
Light to medium ashy hair colours
Blue and pink based, soft, matte, cool skin tones

WARM-MUTED-DEEP
Approachable, Earthy, Woodsy, Rich, Authoritative, Strong Low to medium Contrast between features
Golden, Soft and Opaque qualities
Medium to deep hair colours
Golden based, matte, warm skin tones

WARM-BRIGHT-LIGHT
Glowing, Youthful, Fun, Radiant, Lively, Cheerful, Inviting
High Contrast between features
Light, Bright, Peachy, Fresh and Shiny qualities
Light to medium golden and strawberry hair colours
Yellow based, bright, translucent, warm skin tones
Seasonal Color Analysis : Find out your color season!
- Discover your color season to enhance your natural beauty, simplify your wardrobe coordination, save time and money while boosting your professional presence and confidence.













